Visual of Workflow
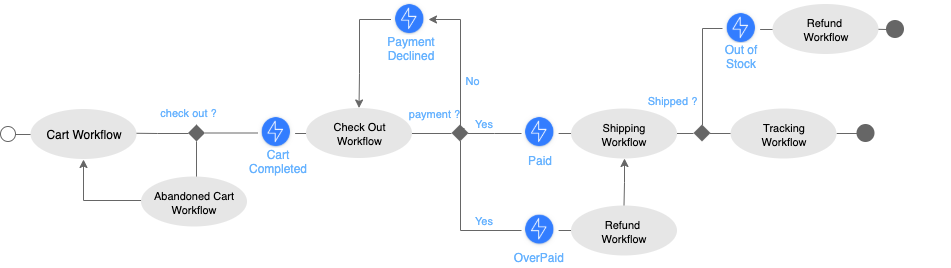
Launch EcommerceWorkflow
EcommerceWorkflow is the main workflow that triggers sub-workflows in the e-commerce process. It is triggered when a user adds an item to a cart. The code to launch this main workflow is:
client.run.withTag(order_id).workflow("EcommerceWorkflow", cart);You have to add this code snippet in your web app. The other worklows will not be in your web application but simply inside your main workflow.
Send Events to EcommerceWorkflow
CartCompleted is sent to the EcommerceWorkflow when the user wants to validate his order. An example of event sent to a subworkflow. The user will then reach the payment process:
client.select.workflow("EcommerceWorkflow").withTag(order_id).send("CartCompleted", cart);The workflow will handle the event through this.wait.event("CartCompleted").forever(); method that will receive the event object as a parameter.
Check-out visual of workflow
The Check Out Workflow is here represented in a flowchart. Several events can be received, resulting in different scenarios.
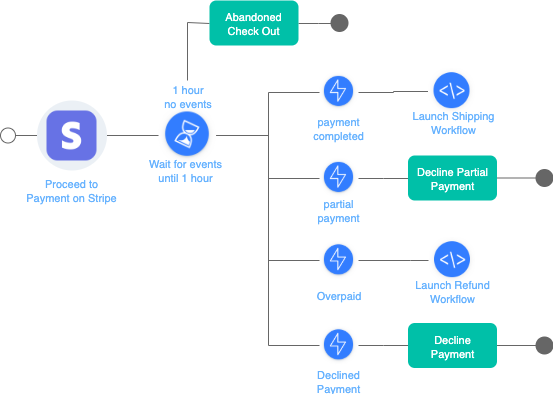
Workflow Steps
- Proceed to payment
- If after one hour, the payment hasn't been completed, then abandon check out
- If the payment is completed, then proceed to shipment
- If the payment is partial, trigger a partial payment task
- If the customer has paid too much, then the overpaid task is triggered
- If the payment is declined, then the checkout is stopped.
Workflow Code
Launch CheckOut Workflow
CheckOutWorkflow is triggered by the main workflow when a user validates item(s) in his cart and wants to proceed to payment. Following the event CartCompleted sent by EcommerceWorkflow, the workflow is directly launched from the EcommerceWorkflow. You don't have to add it in your web application, you simply have to :
const { task } = require("zenaton");
module.exports = task("CheckOutLaunch", async function(order) {
// launch of the workflow from a task
this.run.workflow("CheckOutWorkflow", order);
});Send Events to CheckOut Workflow
PaymentCompleted is sent to the CheckOutWorkflow when the user completes to the payment process. Then, it will trigger the shipping workflow.
client.select.workflow("CheckOutWorkflow").withTag(order_id).send("PaymentCompleted", cart);Structure of the workflow
This workflow is the code that orchestrates the tasks through the Zenaton workflow engine and are then executed on your servers. The workflow is triggered after the order has been completed. Then, the customer proceeds to payment.
const { workflow, } = require("zenaton");
module.exports = workflow("CheckOutWorkflow", {
*handle(order) {
this.stripe = this.connector('stripe', 'your-connector-id');
this.order = order;
this.stripe.post('/v1/charges', {body: {amount: this.order.amount, charge: false, ...}});
const paymentCompleted = yield this.wait.event("PaymentCompleted").for(duration.hours(1));
if (paymentCompleted) {
yield this.run.task("ProceedToShipment", this.order);
} else {
yield this.run.task("AbandonedCheckout", this.order);
}
},
*onEvent(eventName, eventData) {
if (eventName === "PaymentDeclined") {
yield stripe.post(`/v1/issuing/authorizations/${this.order.auth_id}/decline`);
}
if (eventName === "PartialPayment") {
yield stripe.post(`/v1/issuing/authorizations/${this.order.auth_id}/decline`);
}
if (eventName === "OverPaid") {
yield this.stripe.post('/v1/refunds', {body: {charge: this.order.charge, amount: eventData.to_refund}});
}
},
});Abandoned Cart visual of workflow
The Abandoned Workflow is here represented in a flowchart. After one week, without user interaction, the workflow is automatically terminated. To avoid polluting your database, when the users leaves, it automatically removes the cart content. The workflow is triggered when the user exits the website.
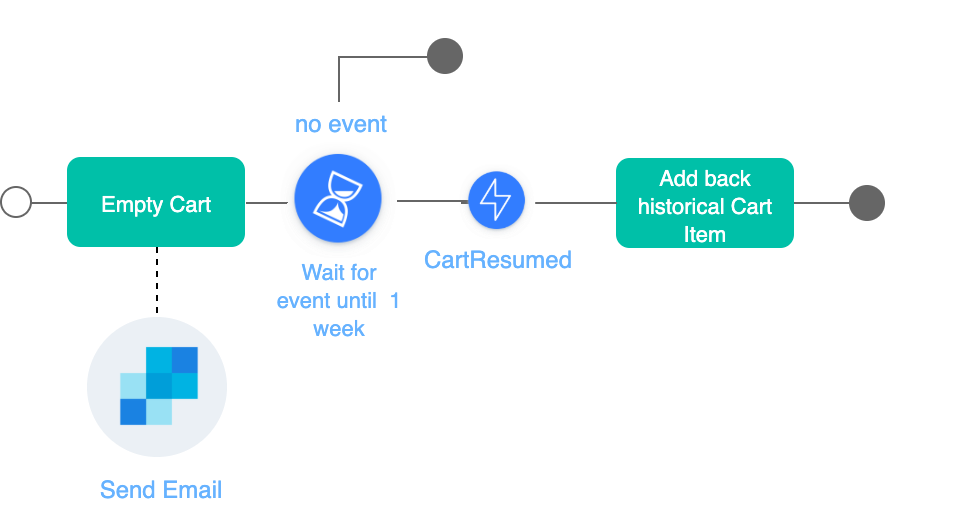
Workflow Steps
- Empty cart to avoid polluting your database
- Send an email to the user for his abandoned cart
- If after more than one week, the user didn't come back to the platform, then the workflow is finished
- If they do come back, the inital item is added back to the cart, allowing him to finish the check out
Workflow Code
Launch Abandoned Cart Workflow
AbandonedCartWorkflow can also be considered as a sub-workflow - it is triggered by the main workflow when a user adds item(s) in his cart but don't proceed to payment - but it is not, it's a classic workflow. If no event CartCompleted is sent in maximum 1 day by EcommerceWorkflow then the workflow is directly launched from the EcommerceWorkflow. You don't have to add it in your web application, you simply have to :
const { task } = require("zenaton");
module.exports = task("AbandonedCartLaunch", async function(order) {
// launch of the workflow from a task
this.run.workflow("AbandonedCartWorkflow", order);
});Send Events to Abandoned Cart Workflow
CartResumed is sent to the AbandonedCartWorkflow when the user comes back to the website within one week. Consequently, it will add back hisotircal cart item.
client.select.workflow("AbandonedCartWorkflow").withTag(order_id).send("CartResumed", cart);Structure of the workflow
This workflow is the code that orchestrates the tasks through the Zenaton workflow engine and are then executed on your servers. Then, the customer proceeds to payment.
const { workflow, duration } = require("zenaton");
module.exports = workflow("AbandonedCartWorkflow", function*(cart) {
const sendgrid = this.connector('sendgrid', 'your-connector-id');
yield this.run.task("RemoveCart", cart.email)
yield sendgrid.post('/mail/send', {body: {"template_id": "abandoned_cart", ...}})
const cart_resumed = yield this.wait.event("CartResumed").for(duration.weeks(1));
if (cart_resumed) {
yield this.run.task("AddInitialCart", cart)
}
});Workflow Executions
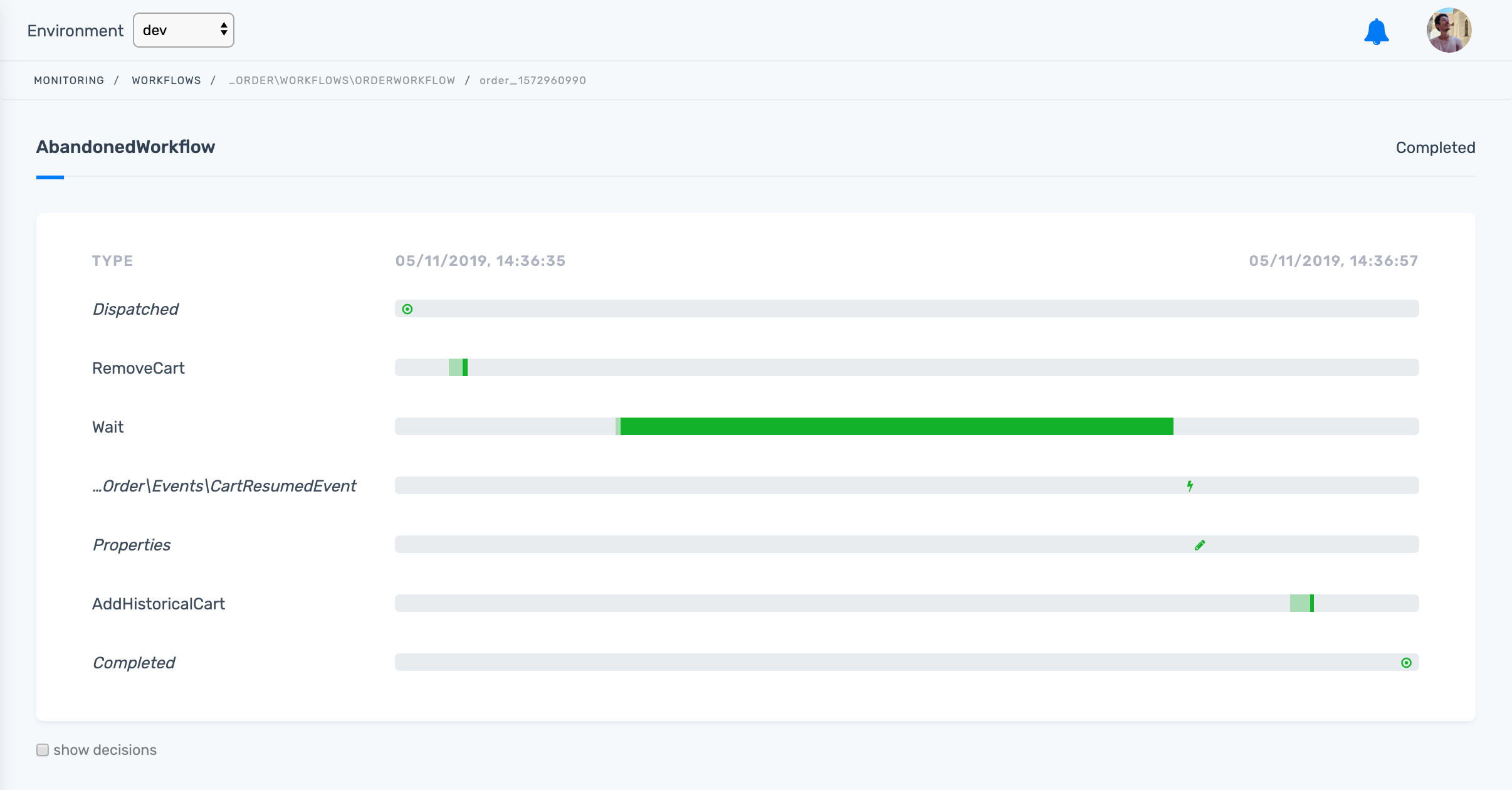
Real-world Examples
Start building workflows
Sign-up and run a sample project Learn more
- Manage cookies
- Terms of Service
- © 2019, Zenaton. All Rights Reserved.